
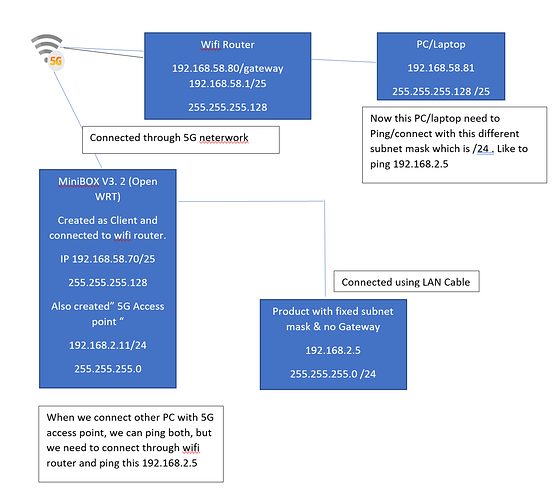
The network and subnet identifier collectively serves as routing prefix, which is expressed in CIDR notation.

The result has a network identifier, subnet identifier, and the host identifier. Or the network identifier bits will be shifted to the right by a number say n. In simple words, few bits from the extreme left of host bits are borrowed towards network bits. The IP network is logically subdivided into subnets. Subnetting is the method that divides the network into two or more subnets. The limitation of network class was removed, hence it is called a classless IP address version 4. With the exponential growth of the Internet and the invention of DNS, a classful IP address became difficult to implement.ĭue to the non-scalability of the classful IP scheme, the subnetting technique and CIDR was devised by IETF in 1993. There were no available blocks between 256 and 65,536, as the subnet mask was limited to 8, 16, and 24 network prefixes in a classful scheme. If we need to connect 2 routers, using a 256 host size block is again a wastage. Class C has a reasonably small network of 256. Similarly, each network block in Class B, there are 65,536 hosts, which is pretty large for any organization. Or you can say, over 2.1 billion IP addresses allocated to 126 organizations only.
#IP MESSENGER DIFFERENT SUBNET FREE#
The first block of 0 and the last block of 127 is not free for general use. Need for Classless IP address version 4Īs we have seen in a classful IP address, Class A address covered a total of 50% available IP addresses in merely 126 usable blocks.
In our previous tutorial, I have explained the Classful IP address, IP address version 4 Classes, and Network ID and Broadcast ID. IP address version 4 is categorized as a Classful and Classless IP address. For example, RMI and a RMI registry, dynamic DNS, CORBA, JINI.Let us discuss the Classless IP address version 4. The simple approach is to identify an existing distributed computing technology that does most of the work for you. Multicast requires special configuration.Įither approach should work on a small network with a limited number of instances.
As M and N grow, the network traffic grows quadratically.īroadcast and Multicast are lossy, especially on busy networks.īroadcast typically doesn't cross network boundaries. Each and every request from M programs goes to N machines and generates N responses. The program accumulates the responses to build a list of all "live" instances. When a program wants to locate instances of the application, it sends a broadcast / multicast request.Įach instance responds to the request giving its details. The applications have to know the name (or address) and port of the registry instance.Įvery instance of the application listens on a well-known "broadcast" or "multicast" address / port. You have to have a way to restore state if the registry restarts. You have to deal with application instances that "go away" without telling the registry. When some machine / program needs to locate an instance of the application, it asks the registry. On startup each instance of the application on the network registers itself with the registry. This service has to be reachable / addressable from every place you want to run the application. Somewhere on the network, you run a Registry Service with a well-known host and port number. This is one of the basic problems in distributed computing, and there are two approaches that work, to a degree: Registry Service


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
